There are two options to increase breast size: autologous fat transplants or implants. While implant-based augmentation has been widely used, a recent study has shown surprising results favoring autologous breast augmentation. These results suggest that the benefits of using a patient’s own tissue and fat have promising benefits for women seeking breast augmentation or reconstruction, both for women recovering from breast cancer and for those seeking breast augmentation for other personal reasons.
Autologous Breast Reconstruction vs. Implant-Based Reconstruction: A Comparison
In a study published in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, women who underwent autologous breast reconstruction (using their own tissue transferred to the breast) reported higher satisfaction with their breasts compared to those who opted for implant-based reconstruction. This finding is unexpected, considering that autologous breast reconstruction is a more complex procedure with a higher rate of complications. Despite these challenges, the study revealed that women undergoing autologous reconstruction had higher satisfaction with their breasts at both six weeks and six months post-surgery.
The analysis included 63 women who chose autologous reconstruction using their own tissues and 75 women who opted for implant-based reconstruction. Before surgery, women in the autologous group had lower scores in all quality of life measures, including satisfaction with breasts. However, the BREAST-Q ratings showed that women in the autologous group had higher scores for satisfaction with breasts at both six weeks and six months post-surgery.
Factors Influencing Satisfaction with Autologous Breast Reconstruction
The higher satisfaction reported by women undergoing autologous breast reconstruction can be attributed to several factors. One possible explanation is that the differences in preoperative scores are not solely related to the timing of reconstruction but also to body type and self-perceived body image and satisfaction. Autologous reconstruction allows for a more natural and personalized result tailored to the patient’s unique body shape and characteristics.
Additionally, the study found that women who underwent immediate reconstruction had higher satisfaction with their breasts compared to those who underwent delayed reconstruction. This suggests that the timing of the procedure can also impact post-operative satisfaction. Furthermore, one-stage reconstruction was associated with higher satisfaction scores than two-stage reconstruction, indicating that a more streamlined approach may lead to better outcomes.
The Impact on Psychological and Sexual Well-being
In addition to higher satisfaction with their breasts, women who underwent autologous breast reconstruction also reported higher scores for psychosocial and sexual well-being. This finding suggests that the procedure not only improves physical appearance but also has a positive impact on overall quality of life. It is crucial to consider these psychological and sexual aspects when discussing breast reconstruction options with patients.
Complications and Recovery
Although autologous breast reconstruction is a more complex procedure with a higher rate of complications, the study found that these complications did not significantly impact overall satisfaction with the results. The researchers expected that women in the autologous group would have lower quality of life scores at follow-up due to the higher complication rate. However, the BREAST-Q ratings painted a different picture, indicating that satisfaction with breasts and other quality-of-life outcomes were not significantly affected by complications.
It is important to note that autologous reconstruction does require a longer operation time and larger surgical wounds compared to implant-based reconstruction. This can result in a longer recovery time, and potentially longer hospital stays. However, despite these challenges, the benefits of autologous reconstruction, including higher satisfaction and improved quality of life, outweigh the risks for many patients.
Breast Reconstruction Options and Outcomes
The findings of this study are part of a larger body of research focused on breast reconstruction options and outcomes. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery® has published a special supplement featuring several original studies on complications and patient-reported outcomes in autologous and implant-based breast reconstruction. These articles highlight the advances and innovations that have improved the quality of care for breast cancer patients.
The supplement is timed to coincide with Breast Cancer Awareness Month and Breast Reconstruction Awareness Day, which are celebrated on October 17th. Breast Reconstruction Awareness Day aims to educate women about post-cancer breast reconstruction options and outcomes, including the federal requirement for insurance coverage for breast reconstruction surgery.
Breast Augmentation Fat Transfers
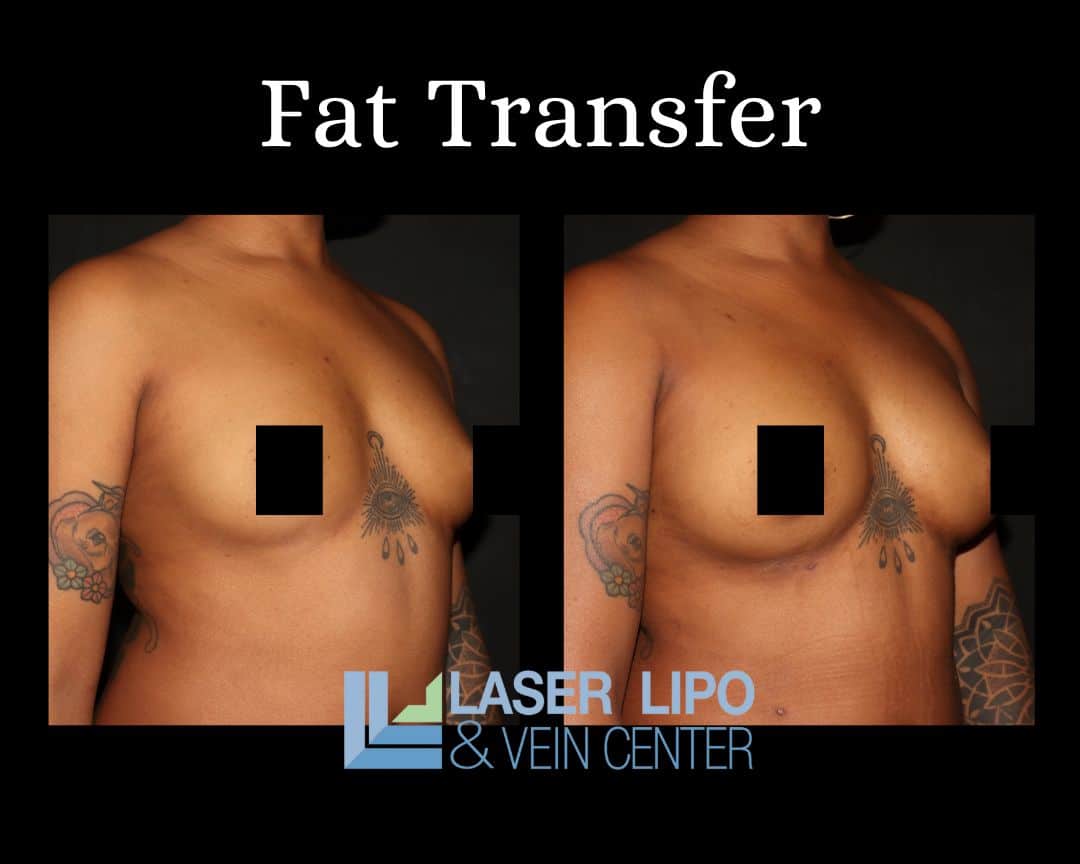
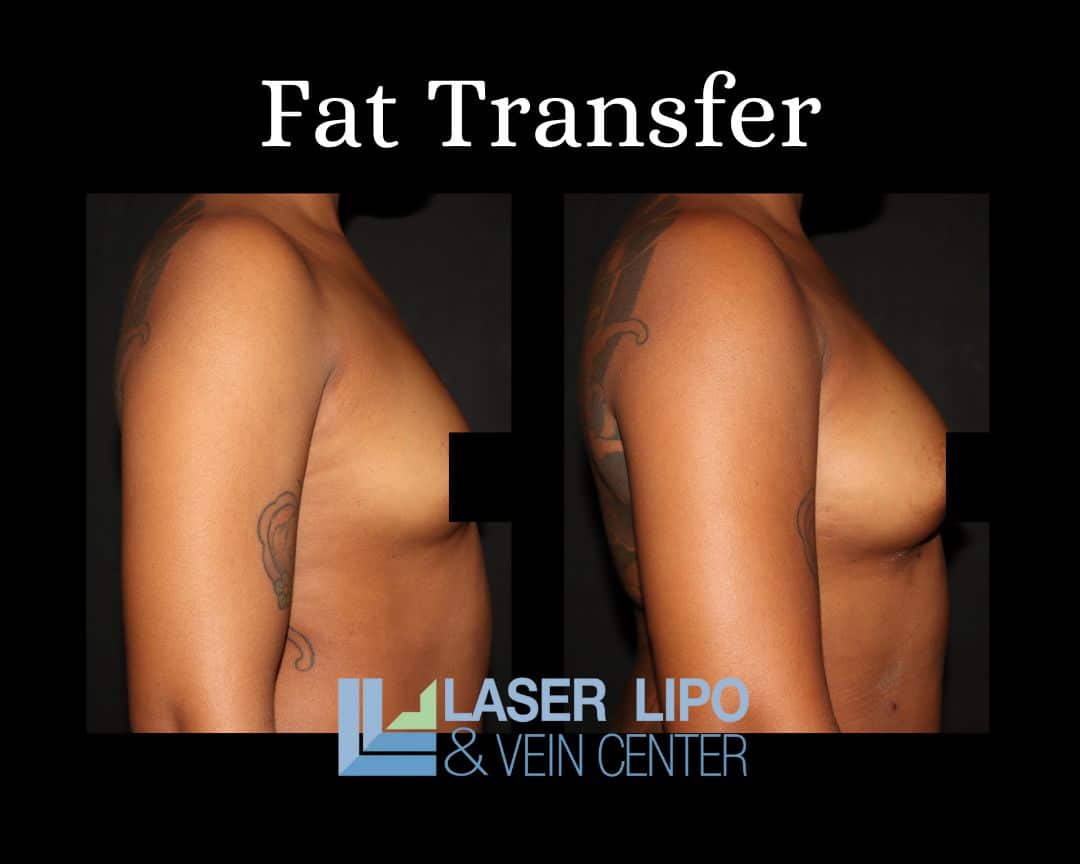
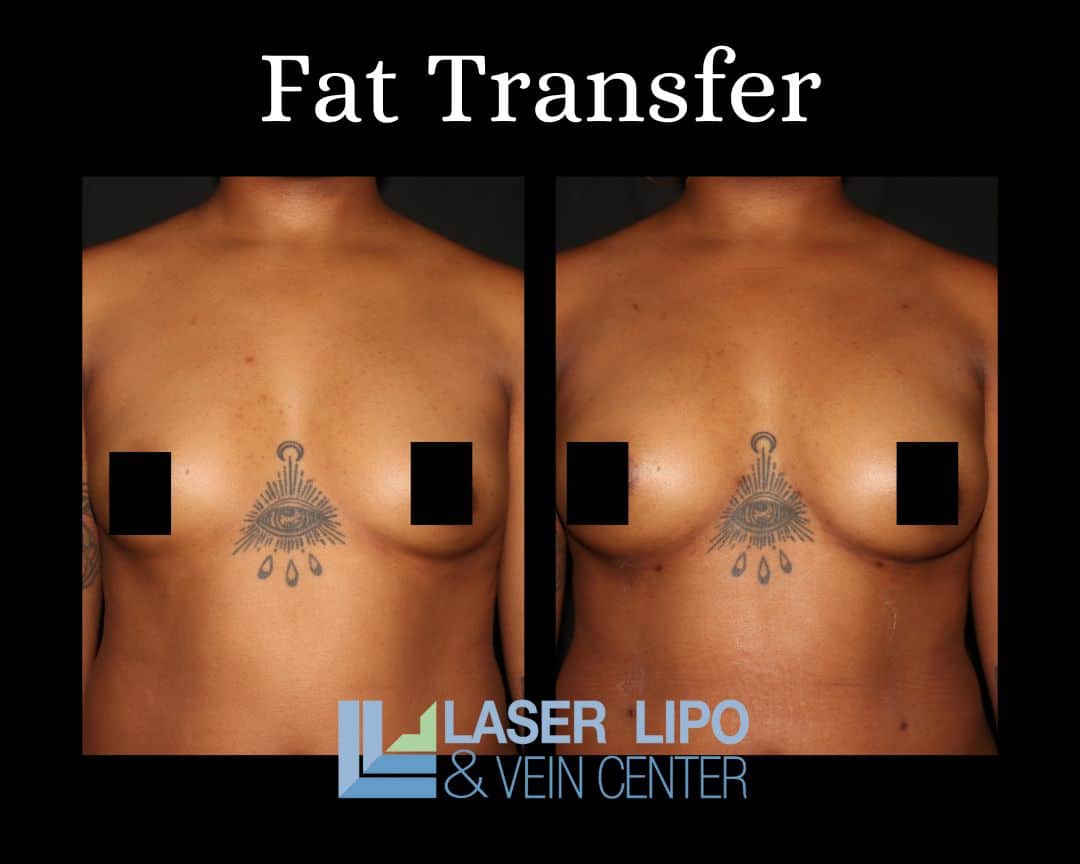
For non-reconstruction patients, fat transfer breast augmentation is a process that involves both liposuction and fat cell transfer to achieve enhanced and natural-looking breasts. Fat deposits are initially removed with the assistance of a liposuction cannula from areas of the body where a patient would like to see greater contour, including the stomach, waist, thighs, or buttocks. Tumescent liposuction is commonly preferred for this St. Louis breast augmentation procedure. Tumescent liposuction provides opportunities for simplified fat removal after the local anesthetic is injected under the skin, and fat deposits can be more easily removed with suction.
Once fat cells are removed, they are thoroughly cleansed before being redistributed directly into the patient’s breasts. Cleansing is performed in combination with adding platelet-rich plasma to the cells, which stimulates collagen and elastin production. Similarly, this mixture promotes faster healing once the procedure is complete. Revitalized fat cells are transferred to the breast through cannula injection and are placed at varying tissue depths for a more natural, overall look. Patients who undergo this procedure enjoy the benefits of both body-shaping due to liposuction and increased breast size, which generally includes a change of half a cup size or a full cup size, depending on patient preference.
In general, patients that undergo fat transfer breast augmentation in St Louis require at least 3 months following the procedure to see complete results. Because this process combines liposuction and fat cell transfers, patients will have multiple injection points that should be tended to after treatment. Most patients report mild discomfort, swelling, and bruising at the injection points for approximately 2-weeks following the procedure. In some cases, patients may experience hardening or numbness of the breasts near the transfer injection sites. Similar to swelling, these symptoms tend to disappear within a couple of weeks after treatment.
What This Means for Breast Augmentation
The findings of these studies suggest that both women seeking post-cancer breast reconstruction and those seeking augmentation without the need for reconstruction can benefit from a fat transfer both short and long-term versus undergoing breast implants. Transferring tissue from one part of the body to another benefits patients with an extremely natural look—similarly, tissue transfer results in breast alteration that feels more natural compared to silicone implants. Risks associated with breast implants are eliminated, as is the risk of allergic reaction when the patient’s own tissue is simply moved to another area of the body.
In general, fat transfer breast augmentation tends to be less expensive than breast implants. It’s important to note that the cost of any procedure will vary from patient to patient. The cost of fat transfer breast augmentation is based on deciding factors, including body mass index, the total amount of fat to be transferred, and the number of areas that will be treated with liposuction.
Conclusion
Autologous breast reconstruction offers numerous benefits for women undergoing breast reconstruction after mastectomy, as well as those seeking augmentation. Women report higher satisfaction with their breasts and overall quality of life compared to implant-based reconstruction. Factors such as body type, self-perceived body image, and the timing of reconstruction play a significant role in determining patient satisfaction.
It is crucial for healthcare providers to thoroughly counsel patients on the advantages and disadvantages of different breast reconstruction and augmentation techniques to manage expectations effectively. By considering the psychological and sexual well-being of patients, healthcare professionals can guide women toward the most suitable reconstruction and augmentation options. Autologous breast reconstruction represents a significant advancement in the field, providing women with personalized, natural-looking results that positively impact their quality of life.
Additional Information from studies:
- Autologous breast reconstruction uses the patient’s own tissues, typically from the abdomen or back, to create a new breast mound.
- Implant-based reconstruction involves the use of silicone or saline implants to reconstruct the breast.
- The BREAST-Q questionnaire is a validated tool to measure patient satisfaction and quality of life outcomes in breast reconstruction.
- Breast Cancer Awareness Month is observed annually in October to raise awareness about breast cancer and promote early detection and treatment.
- Breast Reconstruction Awareness Day (BRA Day) aims to educate women about breast reconstruction options and the importance of insurance coverage for the procedure.